Sp2Sp_light.md 21 KB
业务空间光照辐射网络关系
前置条件
1. 业务空间有所在楼层
2. 业务空间有外轮廓
3. 所在楼层有绑定的模型(即ModelId信息点有值)
处理逻辑
1. 查出所有有所属楼层, 且所属楼层已绑定模型, 并且外轮廓不是null的业务空间
2. 根据所在楼层, 业务空间分区类型来将业务空间分为不同的组 (例如 : A 楼层下的默认业务空间是一组, A楼层下的空调分区是另外一组)
3. 计算每个分组内的业务空间的光照辐射关系
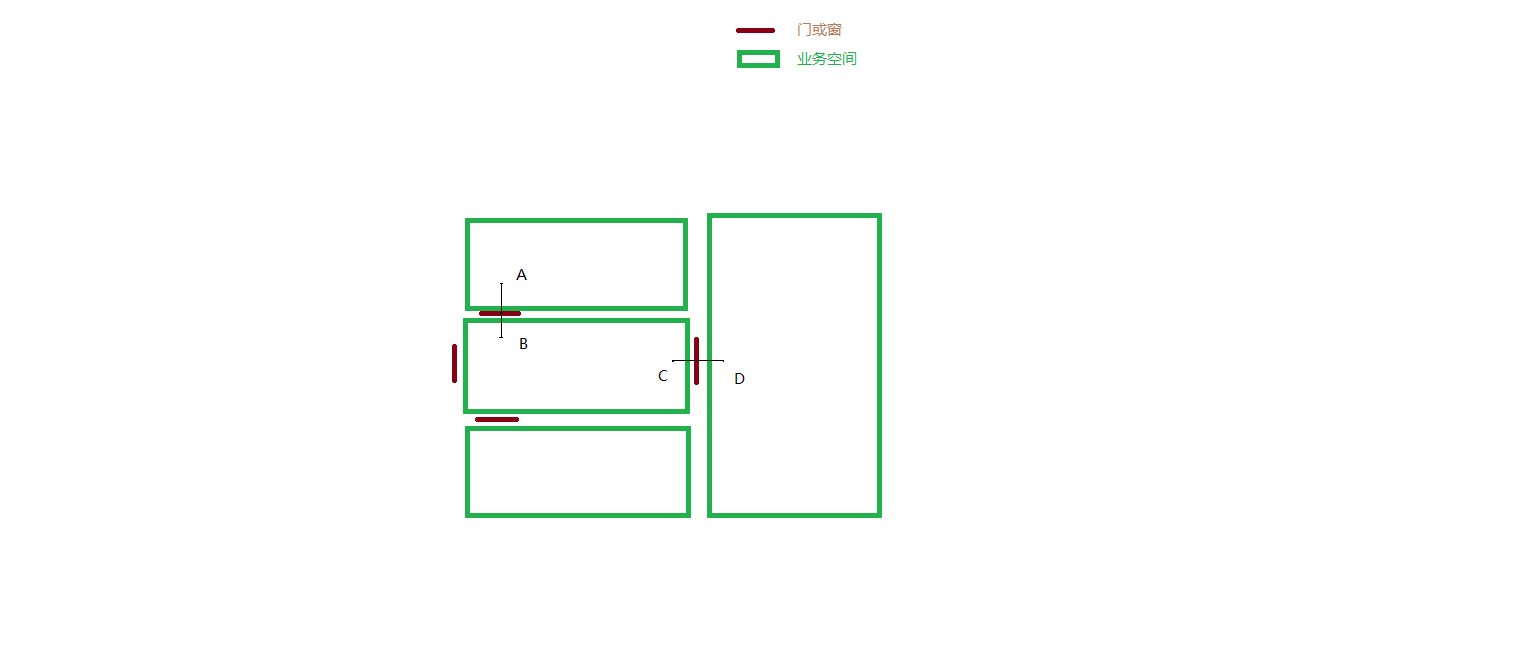
计算光照辐射关系算法 (如下图):
1. 处理逻辑1
1). 获取到该分组所在的楼层下所有的门和窗的轮廓信息(根据楼层ModelId绑定的模型获取)
2). 对于每个门, 在门的中心点上做垂直线段, 获得如图中的点A,B (线段AB长度暂定3m)
3). 然后找到A, B点分别所在的业务空间, 那么认为找到的业务空间有光照辐射网络关系
2. 处理逻辑2
1). 获取该分组所在楼层下的所有元空间轮廓信息(根据楼层ModelId绑定的模型获取)
2). 如果一个元空间同时属于多个业务空间, 则认为这些业务空间有光照辐射关系
4. 将上次计算的结果删除, 然后把新计算出的业务空间光照辐射关系插入关系表中
函数
业务空间轮廓结构
[
[
[
{点坐标},
{点坐标}...
], // 子轮廓的外轮廓
[
{点坐标},
{点坐标}...
], // 子轮廓的第n个需要被排除的轮廓
], // 子轮廓
[
[
{点坐标},
{点坐标}...
]
],
]
源码
create function rel_sp2sp_light(project_id character varying) returns boolean
as
$BODY$
import math
import json
from shapely.geometry import Polygon
from matplotlib.path import Path
column_project_id = 'project_id'
column_location_one = 'location_one'
column_location_two = 'location_two'
column_space_id_one = 'space_id_one'
column_space_id_two = 'space_id_two'
column_zone_type = 'zone_type'
column_added_polygon = 'polygon'
column_id = 'id'
column_bim_location = 'bim_location'
column_floor_id = 'floor_id'
column_object_type = 'object_type'
column_outline = 'outline'
key_x = 'X'
key_y = 'Y'
delta_distance = 200
door_length = 1500
# 获取两点之间的距离
def get_segment_distance(x1, y1, x2, y2):
x_diff = x1 - x2
y_diff = y1 - y2
return math.sqrt(x_diff ** 2 + y_diff ** 2)
# 获取垂直方向的斜率
def get_vertical_k(k):
if k is None:
return 0
if k == 0:
return None
return 1 / k
# 根据点 x, y 计算 y = kx + a 中的 a
def get_a_by_point_k(x, y, k):
if k is None:
return None
return y - k * x
# 在直线 y = kx + a 上找到距离点 base_x, base_y 距离为distance 的坐标点(两个坐标点)
def get_point_by_distance(base_x, base_y, k, a, distance):
if k is None:
return base_x, base_y + distance, base_x, base_y - distance
vector_x1 = math.sqrt(distance ** 2 / (1 + k ** 2))
vector_x2 = -vector_x1
vector_y1 = k * vector_x1
vector_y2 = k * vector_x2
return base_x + vector_x1, base_y + vector_y1, base_x + vector_x2, base_y + vector_y2
# 在直线 y = kx + a 上找到一个点, 该点距离点(base_x, base_y) 长度为 distance, 并且距离vec_x, vec_y最近
def get_point_by_distance_on_segment(base_x, base_y, k, a, distance, vec_x, vec_y):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = get_point_by_distance(base_x, base_y, k, a, distance)
distance1 = get_segment_distance(x1, y1, vec_x, vec_y)
distance2 = get_segment_distance(x2, y2, vec_x, vec_y)
if distance1 > distance2:
return x2, y2
return x1, y1
# 获取输入的两点之间开门之后门的坐标点
# 返回格式
# 如果线段距离小于等于door_length的情况 : x1, y1, x2, y2
# 如果线段距离大于door_length的情况 (两端各开一个门): x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4
def get_points(x1, y1, x2, y2):
# 如果两个点是同一个点
if x1 == y1 and x2 == y2:
return None, None, None, None
# 计算线段的距离
distance = get_segment_distance(x1, y1, x2, y2)
# 计算当前线段的 k
if x1 == x2:
k = None
else:
k = (y1 - y2) / (x1 - x2)
# 计算垂直方向的k
vertical_k = get_vertical_k(k)
# 计算当前线段的 a
a = get_a_by_point_k(x1, y1, k)
# 距离大于delta_distance, 则足够开两个门
if distance > delta_distance:
seg_x1, seg_y1 = get_point_by_distance_on_segment(x1, y1, k, a, delta_distance, x2, y2)
seg_x2, seg_y2 = get_point_by_distance_on_segment(x2, y2, k, a, delta_distance, x1, y1)
vertical_a1 = get_a_by_point_k(seg_x1, seg_y1, vertical_k)
vertical_a2 = get_a_by_point_k(seg_x2, seg_y2, vertical_k)
dest_x1, dest_y1, dest_x2, dest_y2 = get_point_by_distance(seg_x1, seg_y1, vertical_k, vertical_a1, door_length)
dest_x3, dest_y3, dest_x4, dest_y4 = get_point_by_distance(seg_x2, seg_y2, vertical_k, vertical_a2, door_length)
return [dest_x1, dest_x2, dest_x3, dest_x4], [dest_y1, dest_y2, dest_y3, dest_y4]
else:
# 距离太小, 在中间开门
seg_x1, seg_y1 = get_point_by_distance_on_segment(x1, y1, k, a, distance/2, x2, y2)
vertical_a1 = get_a_by_point_k(seg_x1, seg_y1, vertical_k)
dest_x1, dest_y1, dest_x2, dest_y2 = get_point_by_distance(seg_x1, seg_y1, vertical_k, vertical_a1, door_length)
return [dest_x1, dest_x2], [dest_y1, dest_y2]
# 获取Polygon对象
def get_polygon(single_poly):
poly_len = len(single_poly)
poly = []
for i in range(poly_len):
pair = single_poly[i]
poly.append((pair.get(key_x), pair.get(key_y)))
# plpy.info("polygon : {}, {}".format(pair.get(key_x), pair.get(key_y)))
return Polygon(poly)
# 获取Path对象
def get_path(single_poly):
poly_len = len(single_poly)
poly = []
for i in range(poly_len):
pair = single_poly[i]
poly.append((pair.get(key_x), pair.get(key_y)))
# plpy.info("polygon : {}, {}".format(pair.get(key_x), pair.get(key_y)))
return Path(poly)
# 在polygon1包含polygon2的时候, 检测是否polygon1内的空洞也包含polygon2
def is_include(polygon1, poly2):
length1 = len(polygon1)
for i in range(1, length1):
poly1 = get_polygon(polygon1[i])
if poly1.overlaps(poly2):
return True
if poly1.equals(poly2) or poly1.contains(poly2):
return False
return True
def is_sub_outline_overlap(polygon1, polygon2):
poly1 = get_polygon(polygon1[0])
poly2 = get_polygon(polygon2[0])
try:
if poly1.overlaps(poly2) or poly1.equals(poly2):
return True
except Exception as e:
return False
if poly1.contains(poly2) or poly1.equals(poly2):
return is_include(polygon1, poly2)
if poly2.contains(poly1) or poly2.equals(poly1):
return is_include(polygon2, poly1)
return False
# 是否面积有重叠
def is_overlap(polygon1, ispace_polygon):
length1 = len(polygon1)
length2 = len(ispace_polygon)
if length1 == 0 or length2 == 0:
return False
for i in range(length1):
for j in range(length2):
if is_sub_outline_overlap(polygon1[i], ispace_polygon):
return True
return False
# 获取门的轮廓坐标
def get_door_segment(door):
try:
# plpy.info(door.outline)
# door.outline = door.outline.replace('\'', '"')
# plpy.info("outline : {}".format(door.outline))
# door_outline = json.loads(door.outline)
# plpy.info("outline : {}".format(door_outline))
return door.outline[0][0].get(key_x), door.outline[0][0].get(key_y), door.outline[0][1].get(key_x), door.outline[0][1].get(key_y)
except Exception as e:
return 0, 0, 0, 0
# 获取业务空间每个块的最外层轮廓, 组成arr返回, 如果数据不合法发生异常则返回None
def get_outer_polygon_arr(raw_outline):
try:
arr = []
# outline_json = json.loads(raw_outline)
outline_json = raw_outline
for i in range(len(outline_json)):
try:
single_polygon = get_path(outline_json[i][0])
except Exception as ex:
# plpy.info(outline_json[i][0])
plpy.info('eroor getting polygon')
continue
arr.append(single_polygon)
return arr
except Exception as e:
plpy.warning("get outer polygon error")
return []
def dic2obj(d):
"""Convert Dict to Object.
"""
top = type('new', (object,), d)
seqs = tuple, list, set, frozenset
for i, j in d.items():
j0 = j
try:
j0 = json.loads(j0)
except Exception as e:
pass
if isinstance(j0, dict):
setattr(top, i, dic2obj(j0))
elif isinstance(j0, seqs):
setattr(top, i, type(j0)(dic2obj(sj) if isinstance(sj, dict) else sj for sj in j0))
else:
setattr(top, i, j0)
return top
# 将数据库对象转换成python对象
def sqldata2objlist(data):
'''Convert Sqldata to Object list.
'''
return list(map(dic2obj,data))
# 判断一个点是否在多边形数组中的某一个多边形内
def is_point_in_polygons(point, polygon_arr):
try:
for polygon in polygon_arr:
try:
if polygon.contains_points([point], None, -0.0001):
return True
except Exception as ee:
plpy.warning("point in polygon : {0}".format(ee))
return False
except Exception as e:
plpy.warning(e)
return False
# 检查是否已经加过这个关系(单向检查)
def check_is_in_rel(space_adjacent, probe_id, id):
if probe_id in space_adjacent:
rel_set = space_adjacent[probe_id]
if id in rel_set:
return True
return False
# 检查是否关系存在(双向检查)
def check_is_in_rel_bidirection(space_adjacent, probe_id, id):
is_in = check_is_in_rel(space_adjacent, probe_id, id)
is_in = is_in or check_is_in_rel(space_adjacent, id, probe_id)
return is_in
# 将业务空间相邻关系插入map中
def insert_into_rel(space_adjacent, probe_id, id):
if check_is_in_rel_bidirection(space_adjacent, probe_id, id):
return
if probe_id not in space_adjacent:
space_adjacent[probe_id] = set()
rel_set = space_adjacent[probe_id]
rel_set.add(id)
# 将输入数据按照楼层id, 业务空间类型分类
def classify(space_list):
current_floor_id = ''
current_object_type = ''
current_sub_arr = []
space_arr = []
for row in space_list:
if row.floor_id == current_floor_id and row.object_type == current_object_type:
current_sub_arr.append(row)
else:
current_floor_id = row.floor_id
current_object_type = row.object_type
current_sub_arr = [row]
space_arr.append(current_sub_arr)
row.path = get_outer_polygon_arr(row.outline)
for sub_arr in space_arr:
if len(sub_arr) == 1:
space_arr.remove(sub_arr)
return space_arr
# 获取楼层上绑定的真正的模型id
def get_real_model_id(models):
sql_str = ""
for model in models:
sql_str += '\'' + model.model_id + '\','
if sql_str.endswith(','):
sql_str = sql_str[0:-1]
real_model_id_plan = plpy.prepare("select mid.id, file.id fid, file.status from (select id, current_model_id from revit.model_floor where id in ({0})) mid left join revit.model_file file on mid.current_model_id = file.id".format(sql_str), [])
real_model_ids = real_model_id_plan.execute([])
floor_model_dict = dict()
for row in real_model_ids:
floor_id = row.get('id')
model_id = row.get('fid')
status = row.get('status')
if status == 4:
floor_model_dict[floor_id] = model_id
for model in models:
if model.model_id not in floor_model_dict:
models.remove(model)
else:
# plpy.info("mdoel id : {}, {}".format(model.model_id, floor_model_dict[model.model_id]))
model.model_id = floor_model_dict[model.model_id]
# 获取门的数据
def get_door_data(model_id):
door_sql = "select id, outline from graphtype.door where model_id = $1 and type = 'Door' and outline is not null"
door_plan = plpy.prepare(door_sql, ["text"])
door_data = door_plan.execute([model_id])
return sqldata2objlist(door_data)
def get_window_data(model_id):
window_sql = "select id, outline from graphtype.window where model_id = $1 and type = 'Window' and outline is not null and outline != '[]'"
window_plan = plpy.prepare(window_sql, ["text"])
window_data = window_plan.execute([model_id])
return sqldata2objlist(window_data)
# 获取元空间的数据
def get_ispace_data(model_id):
# plpy.info("ispace model id : {}".format(model_id))
# ispace_sql = "select id, outline from zone_ispace where model_id = $1 and outline is not null"
ispace_sql = "select id, outline from revit.space where model_id = $1 and outline is not null"
ispace_plan = plpy.prepare(ispace_sql, ["text"])
ispace_data = ispace_plan.execute([model_id])
return sqldata2objlist(ispace_data)
# 获取业务空间数据, 带所属楼层的信息
def get_sp_floor_data(project_id):
#sql_str = "SELECT sp.id, rel.floor_id, sp.object_type, sp.bim_location, sp.outline FROM zone_space_base sp inner join r_sp_in_fl rel on rel.space_id = sp.id where sp.project_id = $1 and rel.project_id = $1 and outline is not null order by floor_id, object_type"
sql_str = "SELECT sp.id, rel.floor_id, fl.model_id, sp.object_type, sp.bim_location, sp.outline " \
"FROM zone_space_base sp inner join r_sp_in_fl rel on rel.space_id = sp.id left join floor fl on fl.id = rel.floor_id " \
"where sp.project_id = $1 and rel.project_id = $1 and fl.model_id is not null and sp.outline is not null order by floor_id, object_type"
space_data_plan = plpy.prepare(sql_str, ["text"])
space_data = space_data_plan.execute([project_id])
return sqldata2objlist(space_data)
# 根据门的信息计算一个分组内的业务空间是否相邻
def calc_space_adjacent_by_door(space_arr, space_adjacent, space_info):
for space_sub_arr in space_arr:
# space_sub_arr 是一个楼层内的一类业务空间
space_row = space_sub_arr[0]
door_arr = get_door_data(space_row.model_id)
# plpy.info("door : {0}".format(len(door_arr)))
for door in door_arr:
dx1, dy1, dx2, dy2 = get_door_segment(door)
if dx1 == dx2 and dy1 == dy2:
continue
# plpy.info("door location : {}, {}, {}, {}".format(dx1, dy1, dx2, dy2))
x_arr, y_arr = get_points(dx1, dy1, dx2, dy2)
# plpy.info("x : {}, y : {}".format(x_arr, y_arr))
rel_arr = []
for probe_space_row in space_sub_arr:
probe_polygon_arr = probe_space_row.path
space_info[probe_space_row.id] = probe_space_row
for arr_index in range(0, len(x_arr)):
prob_x = x_arr[arr_index]
prob_y = y_arr[arr_index]
is_hit = is_point_in_polygons((prob_x, prob_y), probe_polygon_arr)
if is_hit:
# plpy.info("hit")
rel_arr.append(probe_space_row.id)
break
# 如果关系已经找完的话 退出循环
if len(rel_arr) == 2:
break
if len(rel_arr) == 2:
insert_into_rel(space_adjacent, rel_arr[0], rel_arr[1])
# 根据窗的信息计算一个分组内的业务空间是否相邻
def calc_space_adjacent_by_window(space_arr, space_adjacent, space_info):
for space_sub_arr in space_arr:
# space_sub_arr 是一个楼层内的一类业务空间
space_row = space_sub_arr[0]
window_arr = get_window_data(space_row.model_id)
# plpy.info("door : {0}".format(len(door_arr)))
for window in window_arr:
dx1, dy1, dx2, dy2 = get_door_segment(window)
if dx1 == dx2 and dy1 == dy2:
continue
# plpy.info("door location : {}, {}, {}, {}".format(dx1, dy1, dx2, dy2))
x_arr, y_arr = get_points(dx1, dy1, dx2, dy2)
# plpy.info("x : {}, y : {}".format(x_arr, y_arr))
rel_arr = []
for probe_space_row in space_sub_arr:
probe_polygon_arr = probe_space_row.path
space_info[probe_space_row.id] = probe_space_row
for arr_index in range(0, len(x_arr)):
prob_x = x_arr[arr_index]
prob_y = y_arr[arr_index]
is_hit = is_point_in_polygons((prob_x, prob_y), probe_polygon_arr)
if is_hit:
# plpy.info("hit")
rel_arr.append(probe_space_row.id)
break
# 如果关系已经找完的话 退出循环
if len(rel_arr) == 2:
break
if len(rel_arr) == 2:
insert_into_rel(space_adjacent, rel_arr[0], rel_arr[1])
def calc_space_adjacent_by_ispace(space_arr, space_adjacent, space_info):
for space_sub_arr in space_arr:
# space_sub_arr 是一个楼层内的一类业务空间
space_row = space_sub_arr[0]
ispace_arr = get_ispace_data(space_row.model_id)
# plpy.info("ispace_arr : {}".format(len(ispace_arr)))
for ispace in ispace_arr:
# ispace_outline = json.loads(ispace.outline)
ispace_outline = ispace.outline
rel_arr = []
for probe_space_row in space_sub_arr:
# space_outline = json.loads(probe_space_row.outline)
space_outline = probe_space_row.outline
space_info[probe_space_row.id] = probe_space_row
if is_overlap(space_outline, ispace_outline):
rel_arr.append(probe_space_row.id)
for idx1 in range(len(rel_arr)):
for idx2 in range(idx1 + 1, len(rel_arr)):
plpy.info("rel_arr : {}".format(rel_arr))
insert_into_rel(space_adjacent, rel_arr[idx1], rel_arr[idx2])
try:
# 将下面对数据库的操作作为一个事务, 出异常则自动rollback
with plpy.subtransaction():
space_adjacent = dict()
space_info = dict()
# 获取有所在楼层的所有业务空间, 并按照所在楼层和业务空间类型排序, 方便分组
space_data = get_sp_floor_data(project_id)
get_real_model_id(space_data)
# 给业务空间按照所属楼层和业务空间类型分组
space_arr = classify(space_data)
# plpy.info("space data : {0}, data : {1}".format(len(space_data), space_data))
calc_space_adjacent_by_door(space_arr, space_adjacent, space_info)
calc_space_adjacent_by_window(space_arr, space_adjacent, space_info)
calc_space_adjacent_by_ispace(space_arr, space_adjacent, space_info)
# 删除以前的业务空间相邻关系
delete_plan = plpy.prepare("delete from relationship.r_sp2sp where project_id = $1 and sign = 2 and type = 'sp2sp_RadiationNetwork_1'", ["text"])
delete_plan.execute([project_id])
count = 0
for space_id1, to_space_set in space_adjacent.items():
space1 = space_info[space_id1]
for space_id2 in to_space_set:
# plpy.info("transport relation : {0} , {1}".format(space_id1, space_id2))
count = count + 1
space2 = space_info[space_id2]
delete_duplicate_plan = plpy.prepare("delete from relationship.r_sp2sp where id1 = $1 and id2 = $2 and type = 'sp2sp_RadiationNetwork_1'", ["text", "text"])
delete_duplicate_plan.execute([space_id1, space_id2])
insert_plan = plpy.prepare("insert into relationship.r_sp2sp(project_id, id1, id2, type, sign, zone_type) values($1, $2, $3, 'sp2sp_RadiationNetwork_1', 2, $4)",
["text", "text", "text", "text"])
insert_plan.execute([project_id, space_id1, space_id2, space1.object_type])
plpy.info("sp2sp_light rel : {}".format(count))
return True
except Exception as e:
plpy.warning(e)
return False
else:
return True
$BODY$
LANGUAGE plpython3u VOLATILE
COST 100
select public.rel_sp2sp_light('Pj1101050001')
入参
1. 项目id
返回结果
1. True 计算成功 | False 计算失败
例子
select public.rel_sp2sp_light('Pj1102290002');